Coding Test/BaekJoon
[백준] 16236번: 아기 상어 - java
찬 주
2023. 8. 10. 11:19
문제
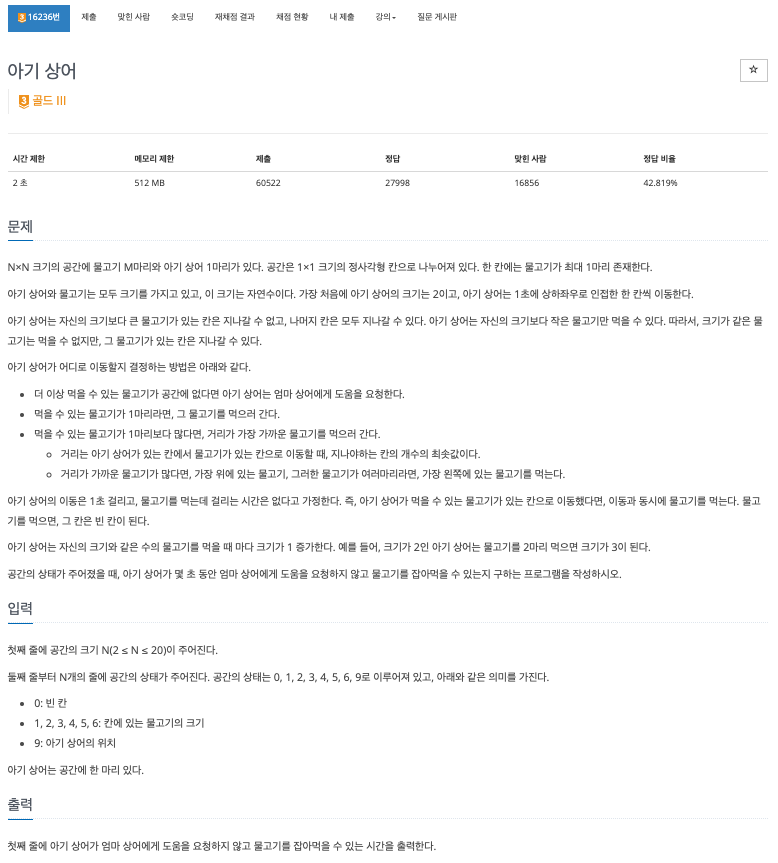
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/16236
16236번: 아기 상어
N×N 크기의 공간에 물고기 M마리와 아기 상어 1마리가 있다. 공간은 1×1 크기의 정사각형 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 한 칸에는 물고기가 최대 1마리 존재한다. 아기 상어와 물고기는 모두 크기를 가
www.acmicpc.net
접근법
최단 거리를 구하는 문제이기 때문에 BFS를 사용한다.
알고리즘
먹을 수 있는 물고기가 남아있을 때까지 BFS를 반복해서 수행한다. 보통은 boolean[][] visited 배열을 사용해 방문 여부를 표시하지만, 나는 물고기를 먹으러 가는데 얼마나 걸리는지를 계산하기 위해 int[][] count를 사용해 해당 지점까지 얼마나 걸리는지를 나타내었다.
BFS를 탐색을 하면서 아기 상어가 먹을 수 있는 물고기를 찾으면 우선 순위 큐에 넣고, 탐색이 끝난 후 우선 순위 큐에서 하나만 꺼내 먹었다는 표시를 해주었다. 여기서 우선 순위 큐는 문제의 조건에서 말한 가장 가까운 물고기를 poll()한다. (만약 한 마리 이상이라면 가장 위에 있는 물고기, 그러한 물고기도 여러마리라면 가장 왼쪽에 있는 물고기) 따라서 Fish 클래스를 만들고, compareTo() 함수를 오버라이딩 해주었다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int answer = 0;
static int[][] map;
static int[][] count;
static int[] dirR = {0, -1, 0, 1};
static int[] dirC = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int sharkSize = 2; // 아기 상어 크기
static int eatCount = 0;
static boolean finish = false;
static Deque<Point> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); // BFS에서 사용할 큐
static PriorityQueue<Fish> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 아기 상어가 먹을 수 있는 물고기들
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new int[N][N];
// input
int edibleFish = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
map[r][c] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (map[r][c] == 9) {
queue.offer(new Point(r, c));
map[r][c] = 0; // 시작 위치도 빈 칸으로
} else if (map[r][c] == 1) {
edibleFish++;
}
}
}
// 먹을 수 있는 먹이가 없는 경우
if (edibleFish == 0) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
// 엄마에게 도움을 요청하기 전까지 반복
while (true) {
start();
if (finish) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
private static void start() {
count = new int[N][N];
// 시작 위치 설정 (방문 하지 않은 곳 = 0으로 판단하기 위해 시작 점을 1로 해준다)
count[queue.peek().row][queue.peek().column] = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point now = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextR = now.row + dirR[i];
int nextC = now.column + dirC[i];
// 범위를 벗어나거나, 방문한 적이 있거나, map에 적힌 수가 상어의 크기보다 크면 제외
if (!rangeIn(nextR, nextC) || count[nextR][nextC] > 0 || map[nextR][nextC] > sharkSize) {
continue;
}
// 빈 칸이 아니고, 아기 상어 크기보다 작은 물고기인 경우
if (map[nextR][nextC] != 0 && map[nextR][nextC] < sharkSize) {
pq.offer(new Fish(nextR, nextC, count[now.row][now.column]));
}
queue.offer(new Point(nextR, nextC));
count[nextR][nextC] = count[now.row][now.column] + 1;
}
}
// 더 이상 먹을 수 있는 물고기가 없는 경우
if (pq.isEmpty()) {
finish = true;
return;
}
Fish fish = pq.poll(); // 아기 상어가 먹은 물고기
answer += fish.distance; // 그 물고기까지 간 거리를 더해준다.
// 먹은 횟수와 아기 상어의 크기가 같은 경우
if (++eatCount == sharkSize) {
sharkSize++;
eatCount = 0; // 먹은 횟수 초기화
}
map[fish.row][fish.column] = 0; // 물고기를 먹었으므로 빈 칸으로 바꿔준다.
queue.offer(new Point(fish.row, fish.column)); // 다음에 아기 상어가 시작할 위치 = 방금 물고기를 먹은 위치
pq.clear();
}
private static boolean rangeIn(int r, int c) {
return (r >= 0) && (c >= 0) && (r < N) && (c < N);
}
static class Point {
int row, column;
public Point(int row, int column) {
this.row = row;
this.column = column;
}
}
static class Fish implements Comparable<Fish> {
int row, column; // 물고기 위치
int distance; // 상어와 물고기까지의 거리
public Fish(int row, int column, int distance) {
this.row = row;
this.column = column;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Fish fish) {
if (this.distance == fish.distance) {
if (this.row == fish.row) {
return this.column - fish.column;
}
return this.row - fish.row;
}
return this.distance - fish.distance;
}
}
}